When building or upgrading a PC, many users focus on the CPU or GPU — but the motherboard chipset plays a crucial role in what your system can do.
In this article, we’ll explain what a chipset is, how it affects compatibility and features, and how to choose the right one based on your goals and budget.
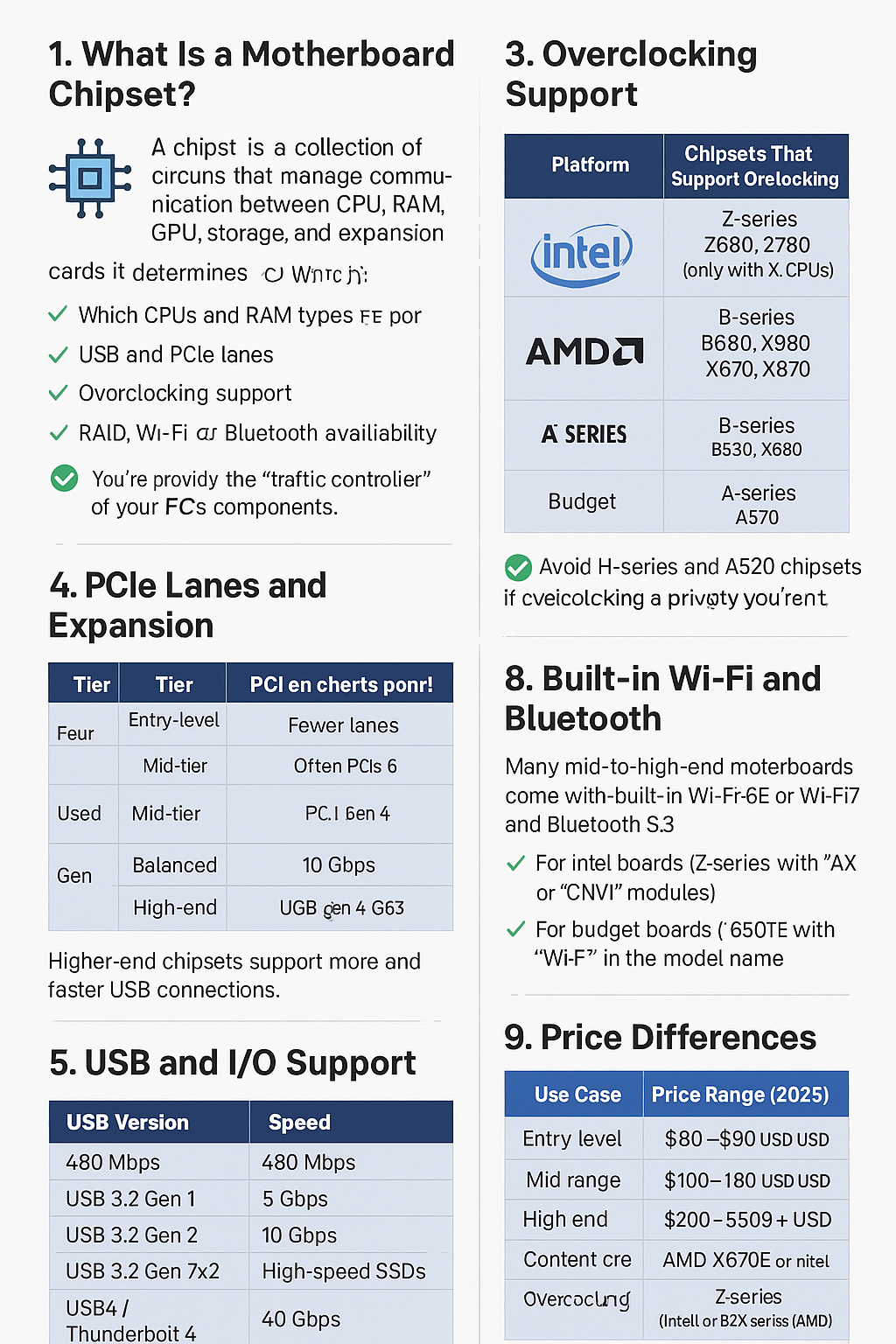
1. What Is a Motherboard Chipset?
The chipset is a collection of circuits that manage communication between the CPU, RAM, GPU, storage, and expansion cards.
It determines:
✅ Which CPUs and RAM types are supported
✅ Number and type of USB and PCIe lanes
✅ Overclocking support
✅ RAID, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth availability
Think of it as the traffic controller of your PC’s components.
2. Intel vs AMD Chipsets (2025 Overview)
Both brands offer multiple chipset tiers:
Intel (LGA 1700/1851 socket platforms)
- Z-series (Z690, Z790, Z890): Full feature set, supports overclocking
- B-series (B660, B760, B860): Mid-range, no CPU overclocking
- H-series (H610, H770): Budget, basic features
- W-series (Workstation)
AMD (AM4 and AM5 socket platforms)
- X-series (X570, X670, X870): High-end, full features, overclocking
- B-series (B550, B650, B850): Mid-range, supports overclocking
- A-series (A520): Budget, no overclocking
✅ Both platforms support DDR4 and DDR5 (depending on chipset and motherboard model)
3. Overclocking Support
Not all chipsets support overclocking.
| Platform | Chipsets That Support Overclocking |
|---|---|
| Intel | Z690, Z790, Z890 (only with K CPUs) |
| AMD | B550, B650, X570, X670, X870 |
If overclocking is a priority, avoid H-series and A520 chipsets.
4. PCIe Lanes and Expansion
Higher-end chipsets offer more PCIe lanes, which allow you to connect:
- Graphics cards
- NVMe SSDs
- Capture cards
- Network adapters
- Sound cards
| Chipset Tier | PCIe Lane Count | Gen Support |
|---|---|---|
| Entry-level | Fewer lanes | Often PCIe Gen 3 |
| Mid-tier | Balanced | PCIe Gen 4 |
| High-end | More lanes | PCIe Gen 4 + Gen 5 |
Example: X670 motherboards support PCIe Gen 5 for GPUs and SSDs.
5. USB and I/O Support
Chipsets affect how many USB ports your system can have — and their speed.
| USB Version | Speed | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| USB 2.0 | 480 Mbps | Mice, keyboards |
| USB 3.2 Gen 1 | 5 Gbps | Storage, webcams |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2 | 10 Gbps | Fast SSDs, docking stations |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 | 20 Gbps | High-speed SSDs |
| USB4 / Thunderbolt 4 | 40 Gbps | High-end displays, eGPUs |
Higher-end chipsets support more and faster USB connections.
6. SATA and NVMe Storage Support
More advanced chipsets:
✅ Allow for more NVMe drives
✅ Support RAID configurations
✅ Use chipset lanes to connect multiple SSDs without GPU performance loss
Some low-end motherboards disable certain ports when others are in use — always check your board’s manual.
7. Built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Many mid-to-high-end motherboards come with built-in Wi-Fi 6E or Wi-Fi 7 and Bluetooth 5.3.
✅ On Intel boards: Look for Z/B series with “AX” or “CNVi” modules
✅ On AMD boards: Look for B650/X670 with “Wi-Fi” in the model name
For budget boards, you may need a separate PCIe card or USB adapter.
8. Form Factor Compatibility
Most chipsets are available on multiple form factors:
| Form Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| ATX | Standard size, most features |
| Micro-ATX | Slightly smaller, fewer slots |
| Mini-ITX | Very compact, limited expandability |
Choose based on your case size and expansion needs — chipset features don’t vary much across sizes.
9. Price Differences
| Chipset Tier | Price Range (2025) |
|---|---|
| Entry-level | $60–$90 USD |
| Mid-range | $100–$180 USD |
| High-end | $200–$500+ USD |
✅ Mid-range B-series chipsets offer the best balance for most users
✅ High-end boards are ideal for enthusiasts, overclockers, and creators
10. Choosing the Right Chipset for You
| Use Case | Recommended Chipset |
|---|---|
| Budget build | AMD A520 or Intel H610 |
| Mid-range gaming | AMD B650 or Intel B760 |
| High-end gaming | AMD X670 or Intel Z790 |
| Content creation | AMD X670E or Intel Z890 |
| Streaming/editing | AMD B650/X670 or Intel Z-series |
| Overclocking | Z-series (Intel) or B/X-series (AMD) |
Always pair the chipset with a compatible CPU, and make sure the BIOS supports your specific model.
Final Thoughts
The motherboard chipset controls everything from connectivity to performance limits — so understanding it is crucial before buying.
✅ Choose a chipset that matches your CPU and your goals
✅ Don’t overspend on features you won’t use
✅ Prioritize BIOS support, expansion options, and form factor
A smart chipset choice makes your build more capable today and more upgradeable tomorrow.