Storage is one of the most important — and often overlooked — components in any PC build. In 2025, you have more options than ever, with blazing-fast SSDs and massive-capacity HDDs available at lower prices.
But which is better for your setup? In this guide, we’ll compare SSDs (Solid State Drives) and HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) in terms of speed, price, durability, and use cases to help you make the right choice.
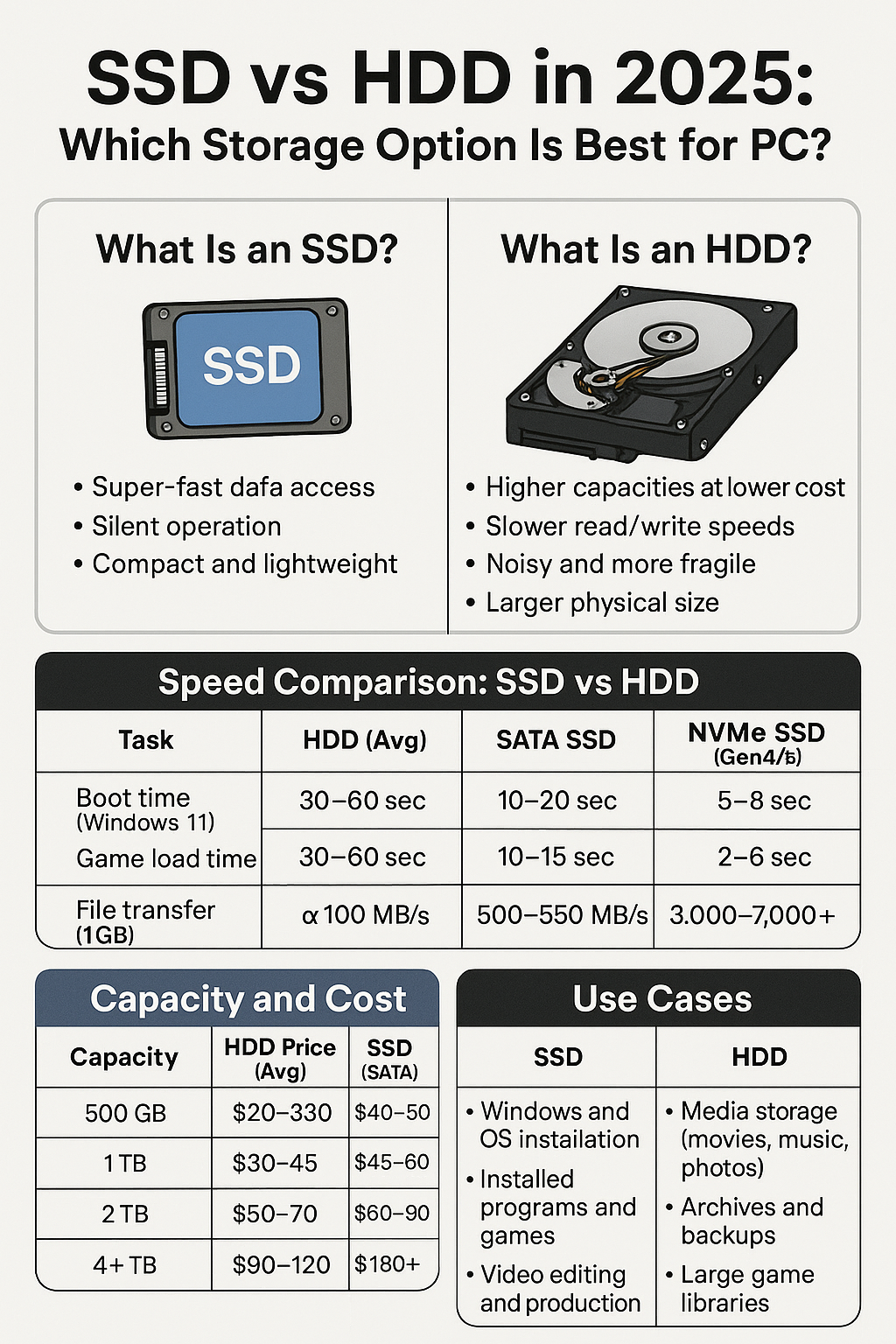
What Is an SSD?
An SSD is a storage device that uses flash memory to store data electronically (no moving parts).
🔹 Key Features:
- Super-fast data access
- Silent operation
- Shock-resistant
- Compact and lightweight
What Is an HDD?
An HDD is a storage device that uses spinning disks (platters) and a mechanical arm to read and write data.
🔹 Key Features:
- Higher capacities at lower cost
- Slower read/write speeds
- Noisy and more fragile
- Larger physical size
Speed Comparison: SSD vs HDD
| Task | HDD (Avg) | SATA SSD | NVMe SSD (Gen 4/5) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boot time (Windows 11) | 30–60 sec | 10–20 sec | 5–8 sec |
| Game load time | 30–60 sec | 10–15 sec | 2–6 sec |
| File transfer (1 GB) | ~100 MB/s | 500–550 MB/s | 3,000–7,000+ MB/s |
Verdict: SSDs (especially NVMe) are up to 70x faster than traditional HDDs in daily tasks.
Types of SSDs (2025)
1. SATA SSD (2.5″)
- Uses SATA III interface (up to 600 MB/s)
- Best for budget upgrades or older systems
2. M.2 NVMe SSD (PCIe Gen 3, 4, or 5)
- Compact, plugs directly into motherboard
- PCIe Gen 4: Up to 7,000 MB/s
- PCIe Gen 5 (2025): Up to 12,000 MB/s
- Ideal for gaming, editing, fast boot
3. External SSDs (USB-C, Thunderbolt)
- Portable and fast
- Great for backups or media libraries
Capacity and Cost
| Capacity | HDD Price (Avg) | SSD Price (SATA) | SSD Price (NVMe) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 GB | $20–$30 | $30–$40 | $40–$50 |
| 1 TB | $30–$45 | $45–$60 | $60–$90 |
| 2 TB | $50–$70 | $70–$100 | $90–$140 |
| 4+ TB | $90–$120 | $120–$180 | $180+ |
Tip: Use HDDs for bulk storage, SSDs for speed-critical tasks.
Durability and Lifespan
| Factor | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Moving parts | Yes (prone to failure) | No (solid state) |
| Shock damage | High risk (drops = data loss) | Very resistant |
| Lifespan | 3–5 years typical | 5–10 years (based on TBW) |
| MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) | 1 million hours | 2+ million hours |
SSDs are more reliable in the long run, especially for laptops or systems that are frequently moved.
Gaming: SSD vs HDD
Modern games require faster load times and large texture files. Some AAA games in 2025 are optimized exclusively for SSDs, including:
- Starfield
- Cyberpunk 2077 (updates)
- Microsoft Flight Simulator
- Next-gen Call of Duty and open-world titles
SSD Required = Better texture streaming, loading times, fewer stutters
When You Should Use an SSD
✅ Windows and OS installation
✅ Installed programs and games
✅ Video editing and production
✅ Virtual machines
✅ Boot drives
Bonus Tip: Always install your OS on an SSD — even a small 256 GB one.
When You Should Use an HDD
✅ Media storage (movies, music, photos)
✅ Archives and backups
✅ Surveillance footage
✅ Large game libraries (secondary drive)
✅ Budget bulk storage
Hybrid Solution: SSD + HDD Setup
This is the best of both worlds:
- SSD (500GB–1TB) for Windows, apps, games
- HDD (2TB–6TB) for media, backups, large files
Most modern motherboards support multiple SATA and M.2 slots, making hybrid setups easy.
Final Thoughts
| Feature | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 🚀 Ultra-fast | 🐢 Slow |
| Price per GB | 💰 Higher | 💸 Cheaper |
| Durability | 💪 More reliable | ⚠️ Fragile |
| Use Case | OS, games, editing, apps | Backups, media storage |
In 2025, SSDs are the standard for performance and reliability — and prices continue to drop. While HDDs still have a place for mass storage, there’s no reason to skip an SSD, especially for your boot drive.
Choose wisely based on your needs, and consider combining both to maximize performance and capacity.