The motherboard is often called the backbone of a computer — and for good reason. It connects all major components, determines compatibility, and plays a central role in your system’s stability, performance, and future upgradability.
Choosing the right motherboard is essential, and this guide will walk you through everything you need to consider before buying one for your next PC build.
What Is a Motherboard?
The motherboard is a large circuit board that holds the CPU, RAM, storage, GPU, and other components together. It also manages communication between all parts of the system.
It doesn’t directly affect performance like a CPU or GPU, but it determines what features and technologies your build can use — such as overclocking, PCIe 5.0, USB-C, or Wi-Fi 6.
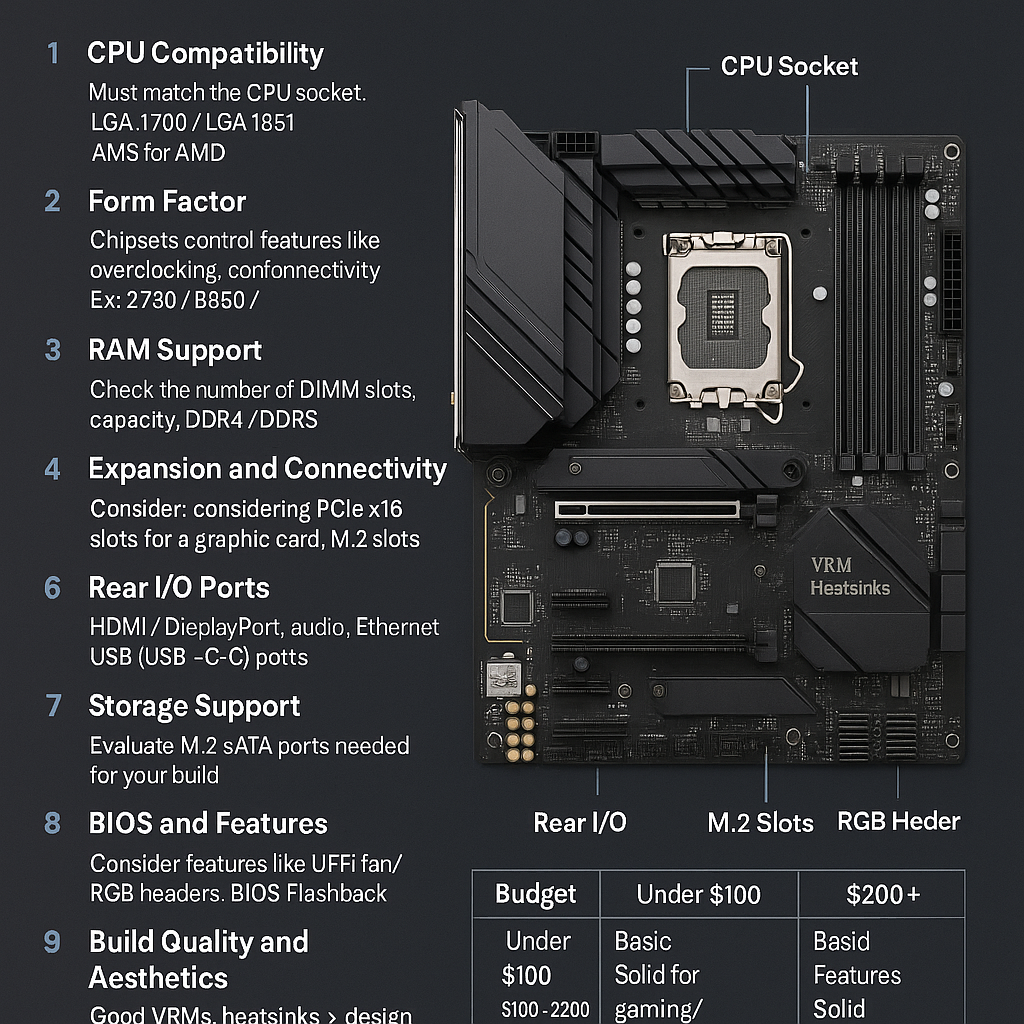
1. CPU Compatibility
Your motherboard must match the socket type of your CPU:
- Intel: Uses LGA sockets (e.g., LGA1700 for 12th–14th Gen, LGA1851 for 15th Gen Arrow Lake).
- AMD: Currently uses AM5 for Ryzen 7000/8000 series.
Always double-check the chipset and BIOS support for your specific processor model — especially if using older stock boards.
2. Form Factor: Size Matters
Motherboards come in various sizes, affecting how many components they can support and what type of case you need.
Common form factors:
| Form Factor | Size (approx.) | Features |
|---|---|---|
| ATX | 12″ x 9.6″ | Full-sized, most expansion slots |
| Micro-ATX | 9.6″ x 9.6″ | Compact, fewer slots |
| Mini-ITX | 6.7″ x 6.7″ | Ultra-small, limited expandability |
Tip: ATX is ideal for most mid/full tower builds. Mini-ITX is great for compact builds but may limit performance options due to space and cooling.
3. Chipset Differences
The chipset affects which features your motherboard supports. It’s especially important for overclocking and connectivity.
For Intel:
- Z790 / Z690: Premium chipsets; support CPU overclocking and PCIe 5.0.
- B760 / B660: Mid-range, no CPU overclocking, but decent features.
- H610: Budget, basic functionality.
For AMD:
- X670 / X670E: High-end with PCIe 5.0 and overclocking.
- B650 / B650E: Mid-range, solid features and PCIe 5.0 in some models.
- A620: Entry-level with fewer ports and no overclocking.
Choose based on your CPU and whether you plan to overclock or need advanced connectivity.
4. RAM Support
Motherboards limit:
- RAM type: DDR4 or DDR5 (can’t mix).
- RAM speed: Only specific speeds are officially supported.
- Capacity: Usually 64GB or 128GB max for most boards.
- Number of DIMM slots: Usually 2 or 4.
Tip:
- DDR5 is faster and more future-proof, but also more expensive.
- Make sure your motherboard matches your RAM generation.
5. Expansion and Connectivity
Motherboards vary widely in their number of expansion slots and ports.
Key expansion options:
- PCIe slots: For GPUs, capture cards, sound cards.
- M.2 slots: For NVMe SSDs.
- SATA ports: For 2.5″ SSDs and hard drives.
- USB headers: For front panel connectivity.
- Wi-Fi/Bluetooth modules: Built-in on premium boards.
Make sure your board has enough PCIe lanes if you’re using multiple GPUs or NVMe drives.
6. Rear I/O Ports
Look for the following on the back of the motherboard:
- USB ports (3.0, 3.2, USB-C)
- Audio jacks (standard 3.5mm or optical)
- HDMI/DisplayPort (for integrated graphics)
- Ethernet (some offer 2.5G or 10G LAN)
- Wi-Fi antennas (on models with built-in wireless)
7. Storage Support
Make sure the motherboard has:
- Enough M.2 slots for fast NVMe SSDs
- Enough SATA ports if you use older SSDs or HDDs
- Support for RAID, if needed
Modern motherboards often support at least one PCIe Gen 4 or Gen 5 M.2 slot.
8. BIOS and Features
Important features to consider:
- UEFI BIOS: User-friendly interface for configuration
- Fan headers: Enough for CPU, case fans, AIO coolers
- RGB headers: For RGB case lighting or fans
- Debug LEDs / Q-Code displays: Helpful for troubleshooting
- BIOS Flashback: Lets you update BIOS without a CPU (great for future upgrades)
9. Build Quality and Aesthetics
More premium motherboards include:
- Reinforced PCIe slots
- VRM heatsinks for better power delivery
- Sleek RGB lighting
- Aluminum I/O covers
These may not improve performance but do enhance reliability and looks.
10. Price and Budget
| Budget Range | What to Expect |
|---|---|
| Under $100 | Basic functionality, no overclocking |
| $100–$200 | Solid features for gaming and productivity |
| $200+ | High-end overclocking, premium features |
Tip: Spend based on your use case. Don’t overspend on a high-end board if you’re not using its features.
Summary: Choosing the Right Motherboard
To choose the best motherboard for your build:
- Match the CPU socket
- Choose a chipset that fits your needs and budget
- Select the right size for your case
- Verify RAM, storage, and GPU support
- Think about expansion and future upgrades
A motherboard won’t directly increase your FPS or load times — but it ensures your components work together reliably and gives you room to grow in the future.